RAM, RCM, FMEA, FMECA and Bad Actor Analysis
These are the reliability tools of the trade.
Whether utilizing PAS 55 and ISO 55001 as your board room to technician reliability framework, AOC deliver the policies, procedures, work processes, knowledge and actions such as preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and condition monitoring tasks, that deliver world class and sustainable, physical asset management.
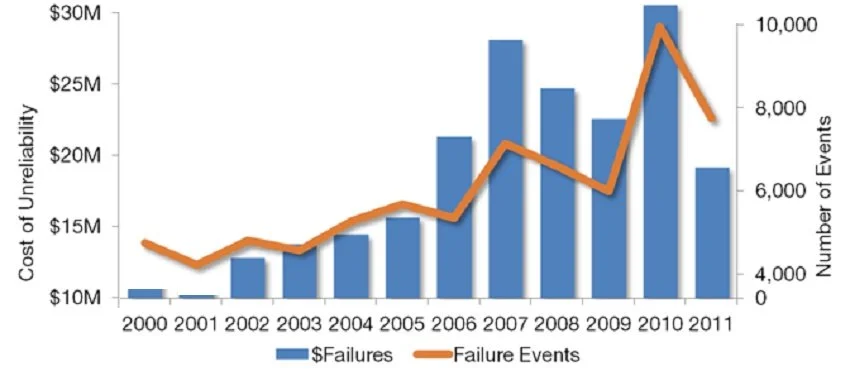
As part of an RCM study, reliability losses can be categorized across all asset families, including electrical systems, rotating equipment, fixed equipment and instrumentation. In the examination of fixed equipment, assets can be further broken down by asset type, such as heat exchangers failures, pressure vessel failures, fired heater failures, and piping failures.
An analysis typically breaks down the basic cause and failure mode into these parts:
- Breakdown - failure to function
- Design - failures related to the design of a part of the process unit or system
- Fouling
- Instrument Malfunction
- Lubrication
- Mechanical Integrity - failures related to leaks
- Operational Error
- Procedures
- Process Related
- Quality Control
- Safety
- Structural
- IOWs - failures related to exceeding safe operating limits
- Unknown Failures
Through reliability engineering studies, AOC ensures continued consistency across failure codes throughout the maintenance work process and supports optimal preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and condition monitoring tasks.
Related Services
A maintenance system designed in which elements work together as a quality system for maximum returns
An interdependent assessment of your people, process, and technologies for a confident path forward
Development of maintenance strategies, recommendations, and plans to implement best practices and increase asset life
Related Tools
Create mechanical integrity (MI) program value rather than it being seen as a necessary cost to minimize.
Is your plant's MI program compliant? Use our checklist to assess your current program against industry standards and receive expert recommendations for improvement.
Related Training
A high level overview introducing Mechanical Integrity and Risk Based Inspection
What are your goals for RBI? How will you measure your success? How will you sustain that success?
How important are they?
How do I use GE APM to perform MI/RBI tasks?
Related Knowledge
Don’t let your RBI program become a "paperwork exercise." Learn how to distinguish between a qualified technical partner and a software-only contractor to ensure true operational safety.
What does a strong refining culture actually look like in practice? Explore seven key attributes, from technical authority to management presence, that transform culture into a powerful risk-control system.
"Good inspection" is not defined by technical tools, but by a leadership choice to allow the truth about equipment condition to surface. Learn why management is the most critical variable in mechanical integrity.
Most PSM loss-of-containment events stem from execution failures, like deferred repairs and ignored inspections, rather than a lack of technical knowledge. Learn why organizational accountability is the key to preventing major accidents.
Is your inspection program reducing risk or just checking boxes? Learn why 100% coverage doesn't guarantee safety and how to shift your focus from activity to true assurance.
The U.S. refining industry recorded nine significant fires and explosions in 2025. While the count is low, incidents at Chevron and HF Sinclair highlight the critical need for robust mechanical integrity and process safety programs.
Can Non-Intrusive Inspection (NII) finally replace vessel entries? Explore the roadblocks to RBI, validated POD data for UT and RT, and a new framework for technical equivalency in modern refinery maintenance.
Why companies overlook Mechanical Integrity: It's expensive, exposes risk, requires specialized knowledge, and is difficult to audit. Learn the 10 structural, cultural, and economic reasons MI is the weakest PSM element.
Discover why equipment failure is the root cause of most catastrophic incidents. Mechanical Integrity (MI) is the non-negotiable foundation that prevents loss of containment and protects your entire PSM system. Learn the 8 reasons MI is essential.
Refinery incidents, especially fires & explosions, appear to be increasing since 2018, though industry-reported safety metrics show a drop. We look at the data, the debate, and why the numbers conflict.


Service Inquiry