Integrity Operating Window Development
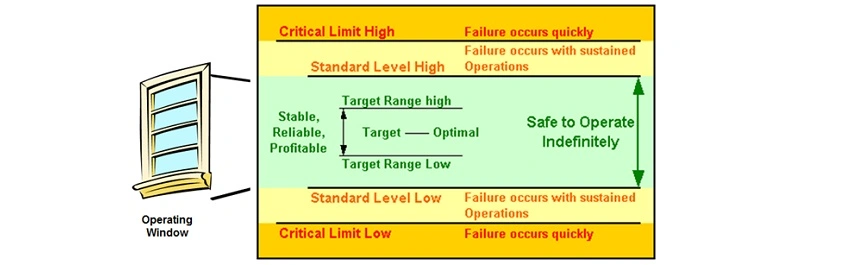
Why develop integrity operating windows?
- New damage mechanisms may be introduced when changes to operating conditions affect key process variables, which can dramatically affect the remaining life of an asset.
- Corrosion rates may accelerate due to crude slate changes or velocity changes, and their effect on the asset may not be recognized until the next scheduled inspection - even if based on risk.
- IOWs identify possible process changes and operating conditions that can affect remaining life and the actions required to mitigate any newly imposed risk.
- Integrating IOWs and real-time corrosion models with your RBI program facilitates the right decision-making-process when these changes occur.
What the standards are saying:
- API RP 580 Section 6.4 - "It may be worthwhile to monitor key process parameters to determine whether operations are maintained within boundaries."
- API 510 Section 6.2 - "The likelihood of failure assessment should be repeated each time equipment or process changes are made."
- API 584 - This second draft of best practices and guidelines for IOWs is under review and has been under development for several years.
What the Owner Operators want:
When considering the implementation of IOWs, prudent Owner Operators want to ensure that the resulting implementation tracks the ongoing development of these standards and is aligned with other industrial standards and recommended practices, such as API 510, APII 570, API RP 571 thru 585, and API STD 653, as well as any in-house standards and risk policies resulting from the implementation.
What is the process of Integrity Operating Window development?
Asset Optimization Consultants implements IOWs following a series of work process steps in line with the Owner Operators best practices. When these are unavailable, AOC has work processes and procedures to augment or deliver new, corporate IOW guidelines. The RBI plan and corrosion study are based on historical operating and inspection data and assumes the assets are all operated within the design specification. With the development of IOWs, your people are equipped with a proper decision-making process to handle changes that occur to your operating conditions. Over time, the life of your asset remains protected.
In general, the process involves:
- Facilitating an IOW review team made up of key stakeholders from the Owner, including inspection, reliability, corrosion engineering, materials engineering, instrumentation, process, operations and maintenance.
- Collecting Data - A myriad of data is required, ranging from process documentation, corrosion studies, and maintenance histories to planned changes in operations and feedstocks. If these are not available, corrosion loops are established as well as identification of required instrumentation for IOW parameters.
- Prioritizing IOWs - The review team will identify and prioritize target IOWs, which can be based on numerous characteristics, loss of reputation, production loss, level and location of risk and consequences as indicted in the RBI study, and on health, safety or environmental impact. Likelihood can be determined from the RBI study or simply the timeframe for an unacceptable event if the process variable is exceeded.
- Recommending IOWs - Each IOW includes a recommended inspection/action response on the part of the operator/inspector/maintenance/reliability engineer.
- Implementing remedial actions - When an IOW is exceeded during operation, the defined personnel can implement the indicated remedial action per the IOW. This action can also include notifying the Reliability Engineering Department, which may need to determine whether additional action, such as a fitness-for-service review, if necessary.
- Integrating IOWs - IOWs should be integrated with other programs within the facility, including but not limited to RBI or inspection program, MOC (management of change), PHA, and of course, Operations.
Related Services
When evaluation of inspection results suggest that an asset is near its end of useful life, Fitness for Service evaluations can determine if the asset us suitable for continued operation.
A maintenance system designed in which elements work together as a quality system for maximum returns
AOC delivers the policies, procedures, work processes, knowledge and actions such as preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance, and condition monitoring tasks.
Related Tools
Is your plant's MI program compliant? Use our checklist to assess your current program against industry standards and receive expert recommendations for improvement.
Create mechanical integrity (MI) program value rather than it being seen as a necessary cost to minimize.
Related Training
A high level overview introducing Mechanical Integrity and Risk Based Inspection
What impact does Risk Based Inspection (RBI) have on my organization?
Is your Risk Based Inspection (RBI) program aligned with the API 580 Recommended Practice? Are you ready for certification?
What's actually going on inside all of that fancy software? An introduction to the API 581 methodology.
A deep dive into quantitative Risk Based Inspection (RBI) as outlined in API 581.
Related Knowledge
Practical guide for implementing a Mechanical Integrity and RBI program for U.S. oil and gas wellfield, gathering, and midstream facilities. Aligns lifecycle asset management, inspection, and risk control with API standards, PHMSA pipeline rules, and OSHA PSM requirements.
Safety-first organizations consistently outperform on reliability when priorities are truly enforced, not just stated.
Organizations that follow the spirit of risk-based inspection rather than its minimum requirements use a definable, structured, auditable process to confirm that an alternate inspection technique provides equal or better risk reduction than a baseline method.
Don’t let your RBI program become a "paperwork exercise." Learn how to distinguish between a qualified technical partner and a software-only contractor to ensure true operational safety.
The U.S. refining industry recorded nine significant fires and explosions in 2025. While the count is low, incidents at Chevron and HF Sinclair highlight the critical need for robust mechanical integrity and process safety programs.
Can Non-Intrusive Inspection (NII) finally replace vessel entries? Explore the roadblocks to RBI, validated POD data for UT and RT, and a new framework for technical equivalency in modern refinery maintenance.
Why companies overlook Mechanical Integrity: It's expensive, exposes risk, requires specialized knowledge, and is difficult to audit. Learn the 10 structural, cultural, and economic reasons MI is the weakest PSM element.
Discover why equipment failure is the root cause of most catastrophic incidents. Mechanical Integrity (MI) is the non-negotiable foundation that prevents loss of containment and protects your entire PSM system. Learn the 8 reasons MI is essential.
Refinery incidents, especially fires & explosions, appear to be increasing since 2018, though industry-reported safety metrics show a drop. We look at the data, the debate, and why the numbers conflict.
PHMSA vs. OSHA: Understanding the Overlap Hydrocarbon facilities like pipelines, refineries, and terminals often fall under both PHMSA (DOT) and OSHA (DOL). Learn where each agency's jurisdiction begins and ends, and how to coordinate your integrity programs for compliance.


Service Inquiry