Asset Value Management vs Asset Performance Management
by Michael Hurley, 2/16/2021 Be the first to commentTags: Asset Performance Management Mechanical Integrity Risk Based Inspection
VP of Technology, Mike Hurley, looks at the concept of Asset Value Management in the financial sector and compares it with Asset Performance Management (APM) with respect to our industry. He goes further to propose a new definition of AVM as applicable to the petrochemical industry and begins the conversation of AVM vs APM.

Today I am going to talk about Asset Value Management (AVM) versus Asset Performance Management (APM). Asset Performance Management has been around for a while, but Asset Value Management is starting to creep into the conversation. In order to understand them we need to know their current definitions:
- AVM – Coming from a traditional financial institution point of view, the typical definition has been, "Value based asset management is about managing the portfolio of assets in capital intensive industries and providing for targeted capital investment."
- APM – According to the Arc Advisory Group, "Asset Performance Management systems act to improve the reliability and availability of physical assets while minimizing risk and operating costs." Note(1)
As we can see from the sources above, traditional AVM seeks to prioritize capital investment and traditional APM seeks to provide better performance through continuous improvement.
There is a problem here. It is illustrated by the questions:
- What if the reliability you are getting out of a particular asset is good enough without APM?
- What if that particular asset is already delivering the value that you need?
These two questions get to the heart of the issue presented and neither of the present definitions address this.
We at Asset Optimization Consultants, Inc. (AOC) want to propose a new definition for Asset Value Management which considers the concerns presented. The definition is:
Managing the value of each existing asset to a predetermined level established by the business requirements. Business requirements can come from various sources such as, but not limited to:
- Profit Margins
- Acceptable Risk Requirements
- Environmental, Health, and Safety Requirements
- Reputational Requirements
This definition addresses the need to provide resources to make some assets provide more value and to allow others to function at their current level without any further investment. This answers the question, of how good is good enough?
The proposed AVM concept is a commonsense approach to managing assets in a chemical plant, refinery, gas plant, etc. Some assets may need to have their performance improved since they need to provide more value and others may function well and provide what is required. This concept is also based upon the "Law of Diminishing Returns". The common definition is, as one production factor increases while the others remain constant, overall production decreases after a certain point. This means that you can only improve the performance of an asset so much; until in begins to adversely affect production, hence value.
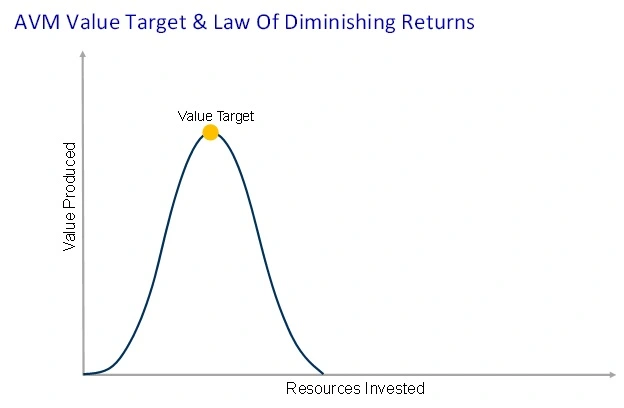
Why does this happen? Performance of assets is generally improved through maintenance tasks and most of these tasks require a shut down. More shut down tasks after a certain point means more downtime. This downtime leads to less value produced.
The mathematical concept is simple and is represented by equation (1):
whereVreturned = Σ 1n Vreturned equipment n(1)
Vreturned – the value produced by the summation of the value of a group of equipment
Vreturned equipment n – the value produced by a single piece of equipment designated n
The Vreturned equipment n is calculated by equation (2):whereVreturned equipment n = POFequipment n ⋅ Dequipment n ⋅ AVRequipment n(2)
POFequipment n – the probability of failure (POF) of loss of function for a single piece of equipment designated n
Dequipment n – the duration of time for which the single piece of equipment is being analyzed
AVRequipment n – the average rate of value produced over the duration
This value is calculated for a particular duration in time; between two chosen dates. Keep in mind that the POF can be the sum of different values for different failure modes for corresponding specific functions. These specific functions could be anything that takes the asset or group of assets out of production for a significant period of time.
Finally, there has to be a comparison of value produced versus the value target for the same duration. This is mathematically represented by equation (3) and equation (4):
orVreturned < Vtarget(3)Vreturned >e; Vtarget(4)
This methodology and these equations can be applied to any level in the asset hierarchy down to the individual asset.
The hard part is determining Vtarget. There are a couple of options to calculate this value:
- Operational Asset Utilization (OAU) can be used to back out a production value
- Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) can also be used to back out a production value
No matter how it is calculated, this value target must come from the management level of the company, plant, or unit. Also, both the target and the value analysis must be compared for the same duration.
AVM as proposed here, is a better way to manage assets with a finite set of resources. It can be used both for targeted capital investment and for asset performance optimization, but it sets a limit. This truly answers the questions; how good is good enough and where will the continuous improvement end?
Let's continue the conversation! I am interested in your feedback on this proposal. Please comment below or contact me directly to start the conversation:
REFERENCES
- Arc Advisory Group, "Asset Performance Management (APM) Defined", https://www.arcweb.com/technologies/asset-performance-management
Add your comment
Related Services
Asset Integrity Management for all asset families - Rotating, Electrical, Instrumentation, and Fixed Assets
An interdependent assessment of your people, process, and technologies for a confident path forward
AOC has delivered thousands of sustainable Risk Based Inspection (RBI) programs earning the trust of owner operators.
Related Tools
Create mechanical integrity (MI) program value rather than it being seen as a necessary cost to minimize.
How well do you know RBI? Take this short quiz to test your knowledge of the API 580 risk-based inspection (RBI) work process.
Is your plant's MI program compliant? Use our checklist to assess your current program against industry standards and receive expert recommendations for improvement.
Related Training
A high level overview introducing Mechanical Integrity and Risk Based Inspection
What impact does Risk Based Inspection (RBI) have on my organization?
Is your Risk Based Inspection (RBI) program aligned with the API 580 Recommended Practice? Are you ready for certification?
What's actually going on inside all of that fancy software? An introduction to the API 581 methodology.
A deep dive into quantitative Risk Based Inspection (RBI) as outlined in API 581.
Related Knowledge
What does a strong refining culture actually look like in practice? Explore seven key attributes, from technical authority to management presence, that transform culture into a powerful risk-control system.
A dysfunctionality found in many refineries, chemical plants, and other production facilities, is a lack of common asset management work processes.
A look at how RBI adds value whether you are just starting out or transitioning from a traditional methodology.
Can Non-Intrusive Inspection (NII) finally replace vessel entries? Explore the roadblocks to RBI, validated POD data for UT and RT, and a new framework for technical equivalency in modern refinery maintenance.
Budget tight? Some Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) risks are too critical to delay. Learn the top 3 RBI risks that can't wait for a budget rebound.
Rate reduction on new projects to support the industry during the current extended downturn.
What are equipment/inspection strategies in relation to mechanical integrity (MI) and risk based inspection (RBI)?
This is a practical approach to incorporating the new PHMSA gas well rules into your integrity program with the rest of your surface and subsurface assets.
Things are always changing. Including your risk profile.
Most PSM loss-of-containment events stem from execution failures, like deferred repairs and ignored inspections, rather than a lack of technical knowledge. Learn why organizational accountability is the key to preventing major accidents.
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2024
- 2025
- 2026


Comments
There are no comments for this article.